Toyota Corolla Cross: Bank 1 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) (P11EA00,P11EC00-P11EF00,P219A00,P219C00-P219F00)
DESCRIPTION
Refer to DTC P003012.
Click here
.gif)
Refer to DTC P030000.
Click here
.gif)
|
DTC No. | Detection Item |
DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
MIL | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
P11EA00 | Bank 1 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P11EC00 |
Cylinder #1 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P11ED00 |
Cylinder #2 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P11EE00 |
Cylinder #3 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P11EF00 |
Cylinder #4 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance (Port) |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P219A00 |
Bank 1 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P219C00 |
Cylinder 1 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P219D00 |
Cylinder 2 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P219E00 |
Cylinder 3 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
| P219F00 |
Cylinder 4 Air-Fuel Ratio Imbalance |
The difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders exceeds the threshold (2 trip detection logic). |
| Comes on |
|
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Fuel System Air Fuel Ratio Cylinder Imbalance MonitorThe ECM uses the air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) and crankshaft position sensor to monitor the difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders caused by differences in injection volumes between the cylinders, leakage in the intake or exhaust system, etc.
When the air fuel ratios of the cylinders are lean or rich with respect to each other, the ECM determines that there is a malfunction, illuminates the MIL and stores a DTC.
Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Sensor 1) Monitoring Method: P11EA00 (for port injection), or P219A00 (for direct injection) is stored primarily when a rich side imbalance is detected.When the system detects a difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders due to fluctuation in the air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) output over 1 engine cycle (2 crankshaft revolutions), the system determines that there is a problem.
Crankshaft Position Sensor Monitoring Method: P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00 and/or P11EF00 (for port injection), or P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and/or P219F00 (for direct injection) are stored primarily when a lean side imbalance is detected.The system monitors the engine speed variation and when the variation becomes large, the system determines that there is a difference in air fuel ratios between the cylinders, which it determines to be a problem.
MONITOR STRATEGY
|
Related DTCs | P11EA: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for port injection of bank 1) P11EC: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for port injection of cylinder 1) P11ED: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for port injection of cylinder 2) P11EE: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for port injection of cylinder 3) P11EF: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for port injection of cylinder 4) P219A: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for direct injection of bank 1) P219C: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for direct injection of cylinder 1) P219D: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for direct injection of cylinder 2) P219E: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for direct injection of cylinder 3) P219F: Air fuel ratio cylinder imbalance monitor (for direct injection of cylinder 4) |
|
Required Sensors/Components (Main) | Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) Crankshaft position sensor |
|
Required Sensors/Components (Related) |
Mass air flow meter sub-assembly Engine coolant temperature sensor Vehicle speed sensor |
| Frequency of Operation |
Once per driving cycle |
| Duration |
20 seconds: Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) monitoring method 30 seconds: Crankshaft position sensor monitoring method |
|
MIL Operation | 2 driving cycles |
|
Sequence of Operation | None |
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
P11EA and P219A: Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Sensor 1) Monitoring Method|
Monitor runs whenever the following DTCs are not stored |
P0010, P1360, P1362, P1364, P1366, P2614 (Motor drive VVT system control module) P0011 (VVT system - advance) P0012 (VVT system - retard) P0013 (Exhaust VVT oil control solenoid) P0014 (Exhaust VVT system - advance) P0015 (Exhaust VVT system - retard) P0016 (VVT system - misalignment) P0017 (Exhaust VVT system - misalignment) P0031, P0032, P101D (Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) heater) P0087, P0088, P0191, P0192, P0193 (Fuel pressure sensor (for high pressure side)) P0101, P0102, P0103 (Mass air flow meter) P0107, P0108 (Manifold absolute pressure) P0117, P0118 (Engine coolant temperature sensor) P0121, P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223, P2135 (Throttle position sensor) P0125 (Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control) P014C, P014D, P015A, P015B, P2195, P2196, P2237, P2238, P2239, P2252, P2253 (Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1)) P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P062D, P21CF, P21D0, P21D1, P21D2 (Fuel injector) P0335, P0337, P0338 (Crankshaft position sensor) P0340, P0342, P0343 (Camshaft position sensor) P0365, P0367, P0368 (Exhaust camshaft position sensor) P0400 (EGR system) P0401 (EGR system (closed)) P0500 (Vehicle speed sensor) P0657, P0658, P2102, P2103 (Throttle actuator) P107B, P107C, P107D (Fuel pressure sensor (for low pressure side)) P1235 (High pressure fuel pump circuit) |
|
Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) status |
Activated |
| Engine speed |
1200 rpm or higher, and less than 2600 rpm |
|
Engine coolant temperature | 75°C (167°F) or higher |
|
Atmospheric pressure | 76 kPa(abs) [11 psi(abs)] or higher |
|
Fuel system status | Closed loop |
|
Engine load | 45% or higher, and less than 70% (varies with engine speed) |
|
Monitor runs whenever the following DTCs are not stored |
P0010, P1360, P1362, P1364, P1366, P2614 (Motor drive VVT system control module) P0011 (VVT system - advance) P0012 (VVT system - retard) P0013 (Exhaust VVT oil control solenoid) P0014 (Exhaust VVT system - advance) P0015 (Exhaust VVT system - retard) P0016 (VVT system - misalignment) P0017 (Exhaust VVT system - misalignment) P0087, P0088, P0191, P0192, P0193 (Fuel pressure sensor (for high pressure side)) P0101, P0102, P0103 (Mass air flow meter) P0107, P0108 (Manifold absolute pressure) P0112, P0113 (Intake air temperature sensor) P0117, P0118 (Engine coolant temperature sensor) P0121, P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223, P2135 (Throttle position sensor) P0125 (Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control) P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204, P062D, P21CF, P21D0, P21D1, P21D2 (Fuel injector) P0327, P0328 (Knock control sensor) P0335, P0337, P0338 (Crankshaft position sensor) P0340, P0342, P0343 (Camshaft position sensor) P0365, P0367, P0368 (Exhaust camshaft position sensor) P0400 (EGR system) P0401 (EGR system (closed)) P0500 (Vehicle speed sensor) P0657, P0658, P2102, P2103 (Throttle actuator) P107B, P107C, P107D (Fuel pressure sensor (for low pressure side)) P1235 (High pressure fuel pump circuit) |
|
Vehicle speed | 30 km/h or more (19mph) |
|
Engine speed | 1200 rpm or higher, and less than 2600rpm |
|
Shift position | 3rd or more |
|
Engine load | 45% or higher, and less than 70% (varies with engine speed) |
|
Engine coolant temperature | 75°C (167°F) or higher |
|
Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) status |
Activated |
| Fuel system status |
Closed loop |
| Auxiliary battery voltage |
11 V or higher |
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
P11EA: Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Sensor 1) Monitoring Method|
Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) monitoring method criteria (rich side imbalance for port injection) |
1 or more |
|
Crankshaft position sensor monitoring method criteria (lean side imbalance for port injection) |
1 or more |
|
Air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) monitoring method criteria (rich side imbalance for direct injection) |
1 or more |
|
Crankshaft position sensor monitoring method criteria (lean side imbalance for direct injection) (first judgement) |
1 or more |
| Crankshaft position sensor monitoring method criteria ( lean side imbalance for port injection) (second judgement) |
0.8 or more |
MONITOR RESULT
Refer to detailed information in Checking Monitor Status.
Click here
.gif)
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$96 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) (Port) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$8D | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Port) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$8E | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Port) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$8F | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Port) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$90 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Port) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$95 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using air fuel ratio sensor (sensor 1) (Direct) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$85 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Direct) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$86 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Direct) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$87 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Direct) |
|
Monitor ID | Test ID |
Scaling | Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $81 |
$88 | Multiply by 0.001 |
No dimension | Monitoring method using crank angle sensor (Direct) |
CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
HINT:
- After repair has been completed, clear the DTC and then check that the vehicle has returned to normal by performing the following All Readiness check procedure.
Click here
.gif)
.gif)
- When clearing the permanent DTCs, refer to the "CLEAR PERMANENT DTC" procedure.
Click here
.gif)
.gif)
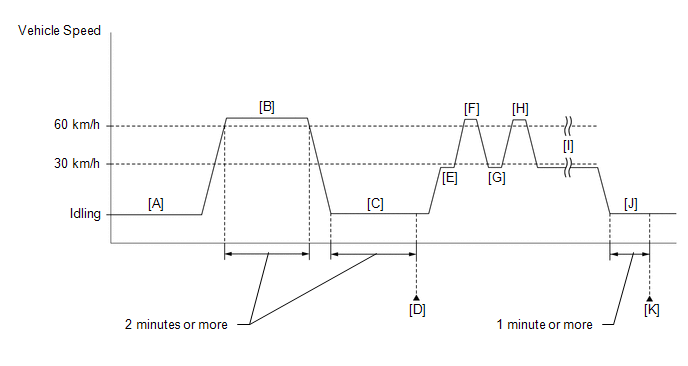
- Connect the GTS to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON.
- Turn the GTS on.
- Clear the DTCs (even if no DTCs are stored, perform the clear DTC procedure).
- Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher [A].
HINT:
The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off and the shift lever should be in P or N.
- Drive the vehicle at 60 km/h (37 mph) or more for 2 minutes or more [B].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
HINT:
It is acceptable to turn electrical loads on while driving.
- Idle the engine for 2 minutes or more [C].
HINT:
The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off and the shift lever should be in P or N.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Trouble Codes [D].
- Read the pending DTCs.
HINT:
- If a pending DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If a pending DTC is not output, perform the following procedure.
- [A] to [D]: Normal judgment procedure.
The normal judgment procedure is used to complete DTC judgment and also used when clearing permanent DTCs.
- When clearing the permanent DTCs, do not disconnect the cable from the auxiliary battery terminal or attempt to clear the DTCs during this procedure, as doing so will clear the universal trip and normal judgment histories.
- Drive the vehicle at less than 30 km/h (19 mph) for 5 seconds or more [E].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Accelerate the vehicle from 30 to 60 km/h (19 to 37 mph) over a period of approximately 10 to 20 seconds.
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
HINT:
Refer to the values of engine load and engine speed in Typical Enabling Conditions before accelerating the vehicle from 30 to 60 km/h (19 to 37 mph).
- Drive the vehicle at 60 km/h (37 mph) or more for 5 seconds or more [F].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Drive the vehicle at less than 30 km/h (19 mph) for 5 seconds or more [G].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Accelerate the vehicle from 30 to 60 km/h (19 to 37 mph) over a period of approximately 10 to 20 seconds.
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
HINT:
Refer to the values of engine load and engine speed in Typical Enabling Conditions before accelerating the vehicle from 30 to 60 km/h (19 to 37 mph).
- Drive the vehicle at 60 km/h (37 mph) or more for 5 seconds or more [H].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Repeat steps [G] through [H] above at least 2 times [I].
- Idle the engine for 1 minute or more [J].
HINT:
The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off and the shift lever should be in P or N.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Trouble Codes [K].
- Read the pending DTCs.
HINT:
- If a pending DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If a pending DTC is not output, perform the following procedure.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine / Utility / All Readiness.
- Input the DTC: P11EA00, P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219A00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 or P219F00.
- Check the DTC judgment result.
GTS Display
Description
NORMAL
- DTC judgment completed
- System normal
ABNORMAL
- DTC judgment completed
- System abnormal
INCOMPLETE
- DTC judgment not completed
- Perform driving pattern after confirming DTC enabling conditions
HINT:
- If the judgment result is NORMAL, the system is normal.
- If the judgment result is ABNORMAL, the system has a malfunction.
- If the judgment result is INCOMPLETE, perform the confirmation driving pattern and check the judgment result again.
- [A] to [K]: Normal judgment procedure.
The normal judgment procedure is used to complete DTC judgment and also used when clearing permanent DTCs.
- When clearing the permanent DTCs, do not disconnect the cable from the auxiliary battery terminal or attempt to clear the DTCs during this procedure, as doing so will clear the universal trip and normal judgment histories.
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
HINT:
- Sensor 1 refers to the sensor closest to the engine assembly.
- Sensor 2 refers to the sensor farthest away from the engine assembly.
- When any air-fuel ratio imbalance is detected, the ECM will perform air-fuel ratio feedback control to make the air-fuel ratio close to the stoichiometric level. This may result in an air-fuel ratio imbalance of normal cylinders and DTCs may be stored.
- Whether malfunctions occur on the port injection side or direct injection side cannot be determined solely by the output DTCs. Inspect every suspected area even if it is not related to the DTCs.
- Read Freeze Frame Data using the GTS. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as Freeze Frame Data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, Freeze Frame Data can help determine if the vehicle was moving or stationary, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred.
PROCEDURE
|
1. | CHECK ANY OTHER DTCS OUTPUT |
(a) Read the DTCs.
Powertrain > Engine > Trouble Codes|
Result | Proceed to |
|---|---|
|
DTC P11EA00, P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219A00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and/or P219F00 is output |
A |
| DTC P11EA00, P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219A00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and/or P219F00 and other DTCs are output |
B |
HINT:
If any DTCs other than DTC P11EA00, P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219A00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and/or P219F00 are output, troubleshoot those DTCs first.
| B |
.gif) | GO TO DTC CHART |
|
| 2. |
READ VALUE USING GTS (FREEZE FRAME DATA) |
(a) Using the GTS, confirm the vehicle conditions recorded in the Freeze Frame Data which were present when the DTC was stored.
Click here .gif)
- Vehicle Speed
- Engine Speed
- Calculate Load
- Accelerator Position
- Short FT B1S1
- Long FT B1S1
- Misfire Count Cylinder #1 to #4
HINT:
When the sum of Short FT B1S1 and Long FT B1S1 is positive, the engine is running lean, and when the sum is negative, the engine is running rich.
|
Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Sensor 1) Monitoring Method (P11EA00 and P219A00) |
Crankshaft Position Sensor Monitoring Method (P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and P219F00) |
Note |
|---|---|---|
| DTCs are output |
DTC is output (Only one DTC relating to a single cylinder is output) |
Malfunctioning of cylinders detected by the Crankshaft Position Sensor Monitoring Method is primarily suspected |
|
DTCs are output | DTCs are output (Multiple DTCs relating to multiple cylinders are output) |
Malfunctioning of cylinders except ones detected by the Crankshaft Position Sensor Monitoring Method is primarily suspected.* |
|
DTCs are not output | DTCs are output |
Malfunctioning of cylinders detected by the Crankshaft Position Sensor Monitoring Method is primarily suspected. |
|
DTCs are output | DTCs are not output |
Malfunctioning of the bank detected by the Air Fuel Ratio Sensor (Sensor 1) Monitoring Method is primarily suspected. |
*: When any air-fuel ratio imbalance is detected, the ECM will perform air-fuel ratio feedback control to make the air-fuel ratio close to the stoichiometric level. This may result in an air-fuel ratio imbalance of normal cylinders and DTCs may be stored.
|
| 3. |
READ DTC OUTPUT |
(a) Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in Confirmation Driving Pattern.
HINT:
- If any misfire count (Misfire Count Cylinder #1 to #4) increases while idling or driving the vehicle, proceed to step 6 (CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM).
- Perform inspections while focusing on the cylinder whose misfire count has increased.
(b) Read the DTCs.
Powertrain > Engine > Trouble Codes|
Result | Proceed to |
|---|---|
|
P11EA00 or P219A00 is output |
A |
| DTC P219A00 and P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 or P219F00 is output |
B |
| DTC P11EA00 and P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00 or P11EF00 is output | |
|
DTC P11EC00, P11ED00, P11EE00, P11EF00, P219C00, P219D00, P219E00 and/or P219F00 is output |
| B |
.gif) | GO TO STEP 6 |
|
| 4. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING GTS (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME) |
(a) Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off and the shift lever should be in P or N.
(b) Enter the following menus.
Powertrain > Engine > Active Test|
Active Test Display |
|---|
|
Control the Injection Volume |
|
Data List Display |
|---|
|
Coolant Temperature |
|
Misfire Count Cylinder #1 |
|
Misfire Count Cylinder #2 |
|
Misfire Count Cylinder #3 |
|
Misfire Count Cylinder #4 |
HINT:
When the "Control the Injection Volume" Active Test is selected (injection volume is 0%), if a misfire count increases, proceed to step 6 (CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM).
(c) Perform the Control the Injection Volume operation with the engine idling.
(d) Check the misfire counts (Misfire Count Cylinder #1 to #4) while decreasing the injection volume in 5% increments.
The cylinder whose misfire count has not increased can be assumed to be running rich. Therefore, perform inspections while focusing on that cylinder.
|
| 5. |
CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK |
(a) Check for exhaust gas leak.
OK:
No gas leaks in exhaust system.
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after repairing or replacing the exhaust system.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | REPAIR OR REPLACE EXHAUST SYSTEM |
|
| 6. |
CHECK INTAKE SYSTEM |
(a) Check the intake system for vacuum leaks.
Click here .gif)
OK:
No leaks in the intake system.
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after repairing or replacing the intake system.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | REPAIR OR REPLACE INTAKE SYSTEM |
|
| 7. |
INSPECT SPARK PLUG |
(a) Inspect the spark plug of the cylinder causing the imbalance.
Click here .gif)
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the spark plug.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | REPLACE SPARK PLUG |
|
| 8. |
CHECK FOR SPARK (SPARK TEST) |
(a) Perform a spark test.
Click here .gif)
HINT:
- If the result of the spark test is normal, proceed to the next step.
- Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the spark plug or ignition coil assembly.
Click here
.gif)
|
| 9. |
CHECK CYLINDER COMPRESSION PRESSURE |
(a) Measure the cylinder compression pressure of the misfiring cylinder.
Click here .gif)
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after repairing or replacing the engine assembly.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | CHECK ENGINE TO DETERMINE CAUSE OF LOW COMPRESSION |
|
| 10. |
CHECK PORT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY OF CYLINDER CAUSING IMBALANCE |
(a) Check the port fuel injector assembly injection [whether fuel volume is high or low, and whether injection pattern is poor].
Click here .gif)
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the port fuel injector assembly.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | REPLACE PORT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
|
|
| 11. |
CHECK DIRECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY OF CYLINDER CAUSING IMBALANCE |
(a) Check the direct fuel injector assembly.
Click here
.gif)
HINT:
Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the direct fuel injector assembly.
Click here .gif)
| NG | .gif) | REPLACE DIRECT FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLY
|
|
| 12. |
CHECK FOR CAUSE OF FAILURE |
(a) If the cause of the problem has not been found even after performing the troubleshooting procedure, perform the inspection below.
(b) Check the intake valve for deposits.
HINT:
As the DTC may have been stored due to deposits on the intake valve, remove the cylinder head sub-assembly and check the intake valve.
|
| 13. |
CLEAR DTC |
(a) Clear the DTCs.
Powertrain > Engine > Clear DTCs(b) Turn the ignition switch off and wait for at least 30 seconds.
|
| 14. |
CONFIRM WHETHER MALFUNCTION HAS BEEN SUCCESSFULLY REPAIRED |
(a) Drive the vehicle in accordance with the driving pattern described in Confirmation Driving Pattern.
(b) Check for DTCs.
Powertrain > Engine > Trouble CodesDTCs are not output.
| NEXT | .gif) | END |

.gif)

